Observed Conditions
Charts with 48 Hours of Conditions
Data is also Available on the API
Conditions are Updated Every 30 Seconds
(Click an Image for Larger View)
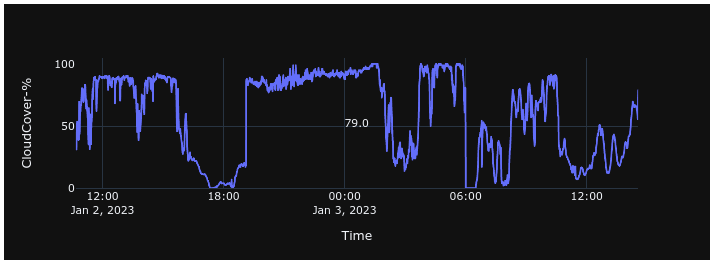
Cloud Cover
Cloud cover is reported as a percentage from 0 to 100, where 0 indicates a completely clear sky and 100 indicates complete cloud coverage.
During daylight operation, cloud cover is determined using image-based sky analysis supported by clear-sky modeling and infrared sky temperature measurements. During nighttime operation, cloud cover is estimated by comparing expected stellar visibility from a reference star catalog against detected stars in the all-sky camera image.
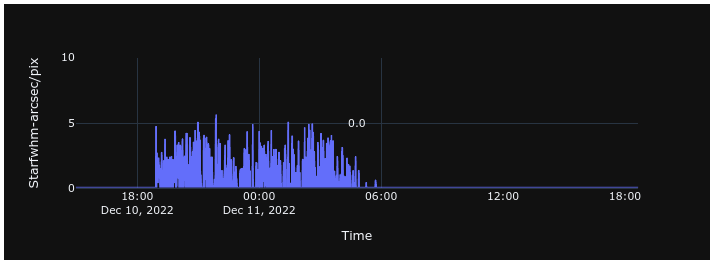
StarFWHM
Star Full Width at Half Maximum (FWHM) is a measure of image quality that reflects the combined effects of atmospheric seeing, optical performance, and tracking accuracy. It represents the apparent angular diameter of a point source spread over the detector.
Values are reported in arcseconds. Lower values indicate sharper stellar images. As a general guideline, FWHM values of approximately 2.0 arcseconds or below are considered indicative of good seeing conditions.
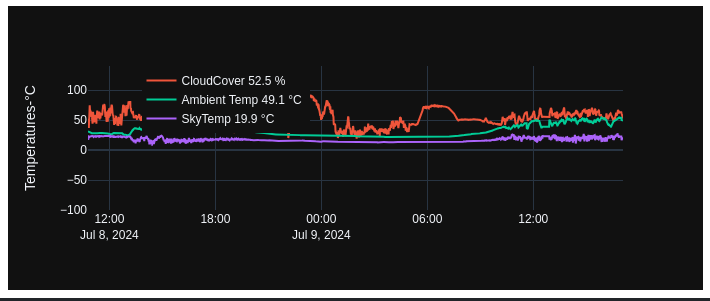
Temperature (Temperature, SkyTemperature)
Ambient temperature and sky temperature are reported in degrees Celsius.
- Ambient temperature is measured directly at the TychoCam™ using an electronic temperature sensor.
- Sky temperature is measured independently using an infrared radiometric sensor and represents the effective radiative temperature of the sky.
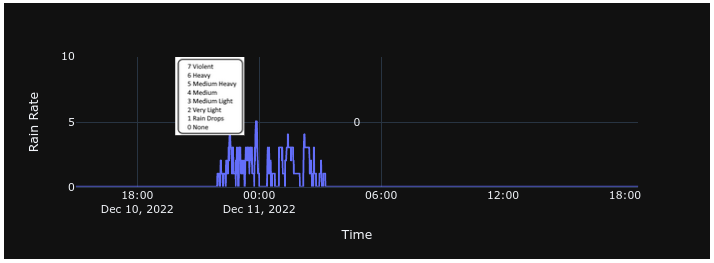
Rain Rate
Rain rate is reported in units of millimeters per hour (mm/hr) and is derived from an infrared rain detection sensor.
For reference, ALPACA defines the following qualitative rain intensity levels:
mm/hr
- Dry - No Rain
- Light - Rain 0.01-0.1
- Moderate - Rain 0.1-0.3
- Heavy - Rain 0.5-2.0
- Violent - Rain 2.0 +
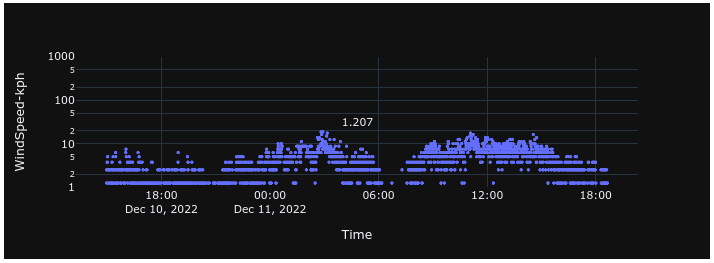
Wind Speed
Wind speed is measured at the TychoCam™ using a mechanical cup anemometer and is reported in kilometers per hour (km/h).

Article
Wind Gust
Wind gusts represent short-duration increases in wind speed above the prevailing wind. A gust is indicated when the peak wind speed significantly exceeds the surrounding lull speeds.
For reporting purposes, TychoCam™ tracks gust activity over a rolling time window of up to 5 minutes to provide a stable indication suitable for observatory safety monitoring.
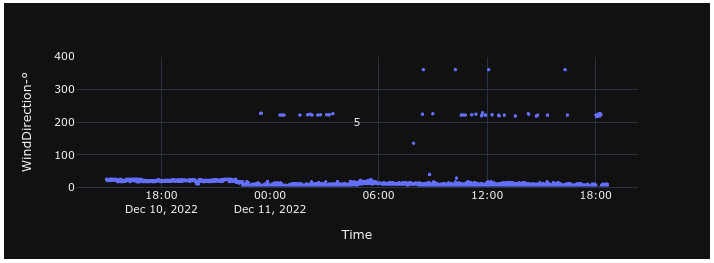
Wind Direction
Wind direction is measured using a mechanical wind vane and reported in degrees, ranging from 0 to 359, measured clockwise from true north.
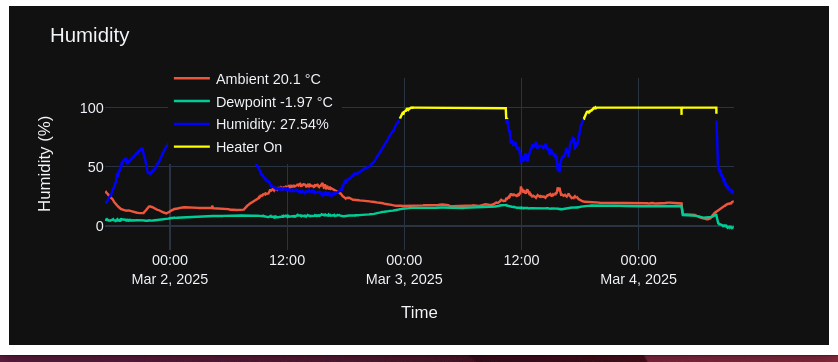
Dewpoint - Humidity
- Dew point is the temperature, in degrees Celsius, to which air must be cooled for water vapor to reach saturation. Dew point is calculated from measured ambient temperature and relative humidity.
- Relative humidity is reported as a percentage and represents the amount of water vapor present in the air relative to the maximum possible at the same temperature. Relative humidity is measured directly using a humidity sensor mounted on the TychoCam™.
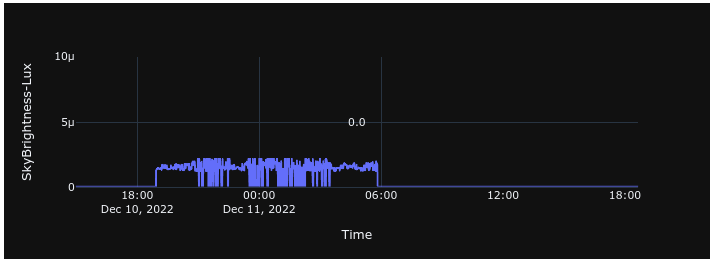
Sky Brightness
Sky brightness is reported as a photometric sky illuminance measurement, expressed in lux, derived from spectrally weighted radiance measurements. Lux is used here as a practical engineering proxy for broadband sky brightness and should not be confused with astronomical magnitude measurements of point sources.
Astronomical magnitudes describe the flux from individual stars relative to defined photometric zero points and are logarithmic in nature. A limiting visual magnitude of approximately 6–6.5 corresponds to the faintest stars detectable by the unaided human eye under ideal dark-sky conditions. This human visual threshold is referenced for context only and is not directly measured by the system.
The sky brightness values reported here represent extended-sky illumination, integrating scattered moonlight, airglow, twilight, cloud reflection, and artificial light contributions across the sensor’s field of view.
| lux | Surfaces illuminated |
|---|---|
| .0001–0.0003 | Moonless Overcast Night Sky |
| 0.001–0.002 | Moonless, clear night sky (pristine) |
| 0.01–0.05 | Clear night with light pollution |
| 0.1–0.3 | Quarter moon, clear sky |
| 0.б5–1.0 | Full moon, clear sky |
| 3–5 | End of civil twilight |
| 100–300 | Heavy overcast daytime |
| 320-500 | Typical office lighting |
| 1000–10,000 | Overcast daytime |
| 10,000–25,000 | Full daylight (not direct sun) |
| 32000–100,000 | Direct sunlight |
Sky Quality
Sky quality is typically expressed in units of magnitudes per square arcsecond (mag/arcsec²), a logarithmic measure of the surface brightness of the night sky. This quantity describes the apparent brightness of the sky background per unit solid angle, independent of individual stars or point sources.
Higher values indicate a darker sky, while lower values indicate increasing sky brightness due to moonlight, twilight, atmospheric scattering, or artificial light pollution.
Sky quality values are often compared to the Bortle Scale, a qualitative classification system for night sky darkness. The numerical values below represent commonly accepted approximate mappings between mag/arcsec² measurements and typical observing environments.
| Quality | Description (Bortle Scale) |
|---|---|
| 22.0 | Exceptional moonless night sky, free of artificial light pollution (Bortle 1) |
| 21.0 | Very dark rural sky; brightest regions of the northern Milky Way (Cygnus–Perseus) highly structured |
| 20.0 | Outer suburbs of a major metropolitan area |
| 19.0 | Suburban sky with widely spaced single-family homes |
| 18.0 | Typical zenith sky brightness at a rural site under a full Moon; Milky Way faint or invisible |
| 17.0 | Typical sky brightness near the center of a major city |
| 13.0 | Zenith sky brightness near the end of civil twilight (Sun ~6° below horizon); only brightest stars visible |
| 7.0 | Zenith sky brightness at sunrise or sunset |